RESPONDING TO THE ENVIRONMENT – HUMANS – LIFE SCIENCES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS From the cellular level to complex societal interactions, our responses to environmental stimuli shape not only our individual experiences but also the collective trajectory of our species. In this blog post, we delve into the fascinating realm of life sciences, exploring how humans respond to their environment through a series of questions and answers.
Activity 1
Questions
Write down the name of the part which:
- Controls heartbeat (1)
- Contains the centres that control balance, muscle tone and equilibrium (1)
- Has centres that interpret what you see (1)
- Coordinates voluntary muscle movements (1)
- Controls body temperature (1) [5]
Answers to activity 1
- Medulla oblongata✔(1)
- Cerebellum✔ (1)
- Cerebrum✔ (1)
- Cerebellum✔ (1)
- Hypothalamus✔ (1) [5]
Activity 2
Questions
Use the diagram of the reflex arc in Figure 6.6 on page 44 to answer the following questions.
- Part B indicates the …
- dendrite of the motor neuron.
- axon of the motor neuron.
- dendrite of the sensory neuron.
- axon of the sensory neuron. (2)
- The correct sequence in which impulses move from the receptor to the effector in the reflex arc in Figure 6.6 is …
- A → B → C → D→ E
- C → A → B → E→ D
- C → B → E → D→ A
- A → D → E → B→ C (2)
- Give the correct term for the following definitions:
- A structure which receives a stimulus and converts it into a impulse
- A structure which responds to a stimulus, e.g. a muscle or gland
- A neuron that carries impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors
- A neuron that carries impulses from the receptors to the central nervous system
- A neuron that carries impulses from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron in the spinal cord
- A very quick, automatic action that involves the spinal cord and not the brain
- The pathway along which an impulse is transmitted to bring about a response to a stimulus during a reflex action 7 × 1 = (7) [11]
Answers to activity 2
- C✔✔(2)
- A✔✔ (2)
- Receptor✔
- Effector✔
- Motor/efferent neuron✔
- Sensory/afferent neuron✔
- Interneuron✔/ connector
- Reflex action✔
- Reflex arc✔ 7 × 1 = (7) [11]
Activity 3
Questions
- Figure 6.13 shows a longitudinal section through the human eye. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
a) Label parts 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. (4)
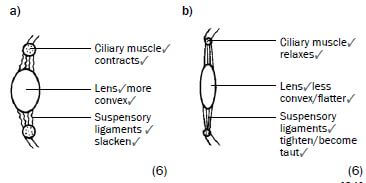
b) Name and describe the process that causes part 1 to dilate (become wider). (5) - Figure 6.14 is a longitudinal section through the human eye. The structures which enable the eye to focus on objects are missing in this diagram. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
Draw a longitudinal section through the missing parts of Figure 6.14 to indicate the appearance of these structures when you are …
a) reading a book. (6)
b) looking at an object more than 6 metres away. (6) [21]

Answers to activity 3
-
a) 2 – Cornea✔
3 – Lens✔
4 – Suspensory ligaments✔
5 – Ciliary muscles✔/ body (4)
b) Pupillary mechanism✔/ pupil reflex
The radial muscles3of the iris contract3and the circular muscles✔relax.✔
The pupil dilates and more light enters the eye.✔ (5) -
 [21]
[21]
Activity 4
Questions
Study Figure 6.17 below and answer the questions that follow.

1. Identify the parts labelled B, C and F. (3)
2. Give the function of the pinna. (2)
3. Write the letter of the part which:
a) contains receptors for balance. (1)
b) equalises the pressure on either side of part B. (1)
c) transmits impulses to the brain. (1)
4. Describe how hearing occurs. (8) [16]
Answers to activity 4
1.
B -Tympanic membrane✔
C – Malleus/hammer/an ossicle✔
F – Cochlea✔(3)
2. It directs sound waves✔ into the auditory canal✔. (2)
3.
a) D✔
b) G✔
c) E✔ (3)
4.
- Sound waves are directed into the auditory canal✔ by the pinna✔.
- The sound waves make the tympanic membrane vibrate✔ and the vibrations are passed on to the ossicles✔ in the middle ear.
- The ossicles make the oval window vibrate✔ and this causes pressure waves to be set up in the inner ear.
- These vibrations also cause the organ of Corti✔ to be stimulated and it generates impulses which are sent to the cerebrum✔ along the auditory nerve✔.
- The cerebrum interprets the impulses as sound✔. (8) [16]

 [21]
[21]